Understanding the Link Between PTSD And Addiction
How Past Traumas And PTSD Can Influence Addiction And Its Treatment

Trauma is a common experience among individuals with addiction, and it can play a significant role in the development and maintenance of substance use disorders. Trauma can cause a range of physical and psychological symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These symptoms can make it more difficult for individuals to manage their addiction and increase the risk of relapse. In this blog post, we will explore how past traumas and PTSD can worsen addiction to alcohol and other substances.
The Link Between Physical and Psychological Trauma and Addiction
Trauma is an event that causes an individual to experience intense fear, helplessness, or horror. Trauma can be caused by a variety of events, including natural disasters, accidents, violence, and physical or sexual abuse. Trauma can cause a range of physical and psychological symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
Trauma is a common experience among individuals with addiction. In fact, research suggests that up to 75% of individuals seeking treatment for substance use disorders have a history of trauma. Trauma can lead to a range of negative emotions, such as fear, anger, and shame. Individuals may turn to substances as a way to cope with these emotions and the distressing memories associated with their trauma.
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Addiction

Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a condition that can develop after an individual experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. PTSD can cause a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance behaviors. PTSD is also strongly associated with addiction. Research has shown that individuals with PTSD are at a higher risk of developing substance use disorders than those without PTSD.
PTSD can worsen addiction in several ways. First, PTSD can increase the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Individuals with PTSD may experience more intense cravings and physical symptoms when attempting to stop using substances. Second, PTSD can make it more difficult for individuals to manage their emotions. Individuals with PTSD may turn to substances as a way to cope with negative emotions, such as anxiety and depression. Finally, PTSD can increase the risk of relapse. Individuals with PTSD may be more likely to experience triggers that lead to substance use, such as reminders of their trauma.
Alcohol Addiction and Alcoholism and Trauma
Alcohol is a commonly used substance among individuals with a history of trauma. Alcohol can temporarily reduce anxiety and other symptoms of trauma, making it an appealing coping mechanism for individuals with PTSD. However, alcohol use can also worsen the symptoms of trauma and increase the risk of addiction, especially if it’s significant alcohol addiction or alcoholism.
Alcohol use can have a range of negative effects on individuals with trauma and PTSD. For example, alcohol can interfere with sleep, leading to more frequent nightmares and other sleep disturbances. Alcohol use can also impair memory and cognitive function, making it more difficult for individuals to process and manage their trauma. Finally, alcohol use can interfere with the effectiveness of PTSD treatment, making it more difficult for individuals to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of addiction.
Other Substances of Abuse and Trauma
Trauma can also worsen addiction to other substances, such as opioids, stimulants, cocaine, and even prescription medications. For example, individuals with trauma may turn to opioids as a way to cope with physical pain or emotional distress. Opioid use can provide temporary relief from pain and other symptoms of trauma, but it can also increase the risk of addiction and overdose.
Stimulants, such as cocaine and methamphetamine, can also worsen the symptoms of trauma and increase the risk of addiction. Stimulant use can cause anxiety, paranoia, and other symptoms that can exacerbate the effects of trauma. Stimulant use can also interfere with sleep and exacerbate symptoms of PTSD.
Treatment for Co-Occurring Addiction, Alcohol Dependence, and PTSD Trauma
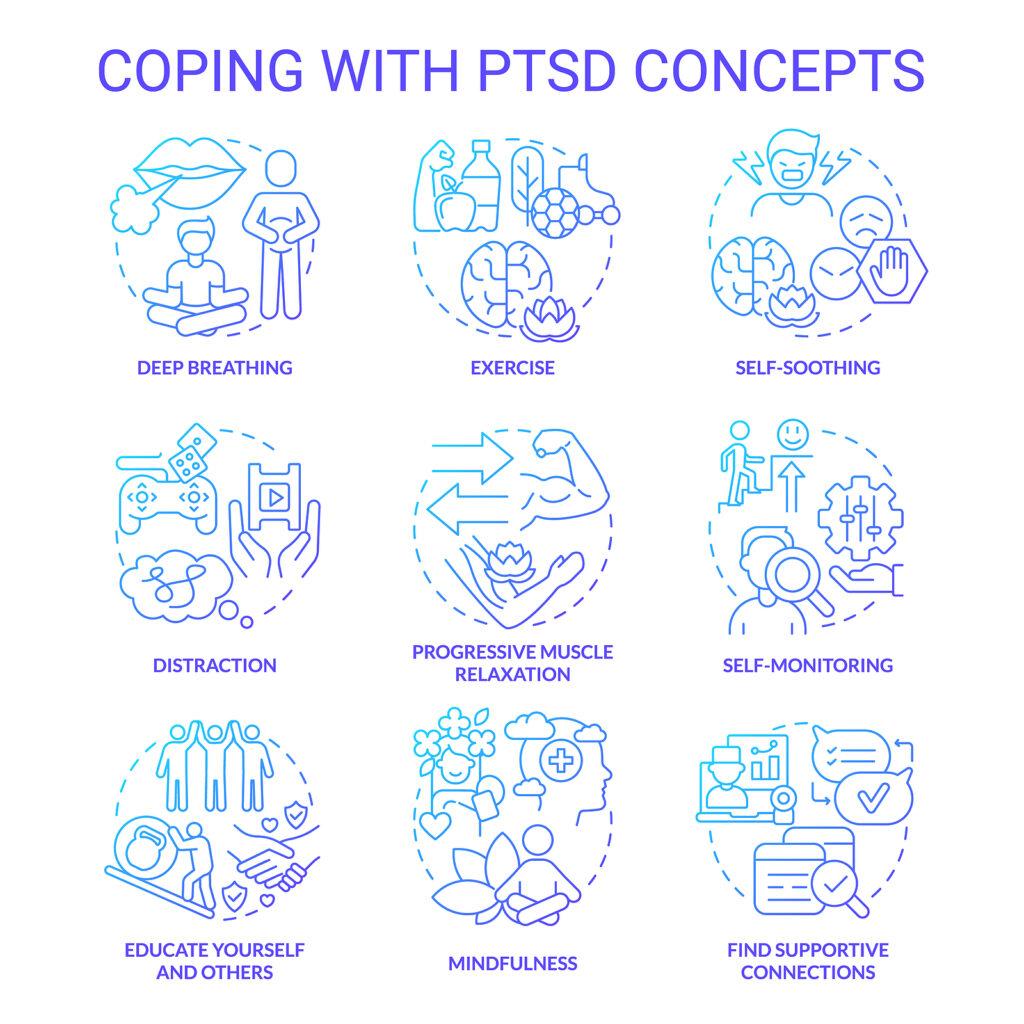
Treatment for trauma and addiction is complex and often requires a multi-faceted approach. Effective treatment should address both the underlying trauma and the substance use disorder. Treatment may include individual and group therapy, medication-assisted treatment, and holistic therapies, such as mindfulness and yoga.
Individual and group therapy can help individuals with trauma and addiction to process their experiences and develop coping skills to manage their symptoms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other evidence-based therapies can be effective in treating PTSD and addiction. These therapies can help individuals to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthy coping skills.
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can also be effective in treating addiction and PTSD.
MAT combines medication, such as buprenorphine or naltrexone, with therapy to reduce cravings and improve treatment outcomes. MAT has been shown to be effective in treating opioid use disorder and alcohol use disorder.
Holistic therapies, such as mindfulness and yoga, can also be effective in treating trauma and addiction. These therapies can help individuals to develop a greater sense of self-awareness and self-regulation, which can reduce the symptoms of PTSD and improve treatment outcomes.
Trauma and addiction are complex conditions that can be difficult to manage. However, effective treatment is available for individuals with these conditions. Treatment should be tailored to the individual’s unique needs and should address both the underlying trauma and the substance use disorder. By addressing the root causes of addiction, individuals with trauma can achieve lasting recovery and improve their overall well-being. It is important to recognize the link between trauma and addiction and to seek help if you or a loved one is struggling with these conditions. With the right treatment and support, recovery is possible.
Begin PTSD Treatment in NYC, Manhattan
Navigating addiction while also working through past trauma can sometimes take support. As an addiction therapist, I would be happy to offer this support from my NYC, Manhattan-based therapy practice with in-person and online options. You can start your therapy journey by following these simple steps:
- Contact Stephen Gilman, MD
- Learn more about me and my approach to PTSD treatment
- Start managing addiction and past pain in a healthy way
Other Services Offered with Stephen Gilman, MD – Addiction Psychiatrist in NYC, Manhattan
PTSD treatment isn’t the only service I offer. I understand addiction can cover a wide range of topics. This is why I’m happy to also offer mental health support in a variety of other services. Other services offered include opioid addiction treatment, general psychiatry, adult psychiatry, and meth addiction treatment. I’m also happy to offer young adult psychiatry and cocaine addiction. In addition, I also offer behavioral addiction treatment, drug addiction treatment, and marijuana addiction treatment. Learn more about me or visit my blog for more helpful info.



